How to Learn Full-Stack Web Development in 2025 (With Projects)
In 2025, the average salary for a full-stack developer is between 120K and 150K. Senior positions often exceed 250K in tech giants.
As a result, full-stack development remains one of the most rewarding paths for anyone looking to get into tech.
As technologies progress, full-stack development is no longer just about learning a few languages. It’s about understanding user requests and using modern technologies to deliver maintainable, scalable, and secure web applications.
Whether you want to freelance, land your first developer job, or launch your own SaaS, mastering the fundamental skills gives you the flexibility and confidence to build real products from scratch.
In this guide, you’ll get a clear roadmap for learning full-stack web development, including the essential skills, a step-by-step learning path, project ideas, and the best resources and tools to accelerate your journey.
Learn Coding in the AI era
First of all, let's talk about the one question everyone is asking:
Is it still worth it to learn coding in the AI era?
The short answer is, yes.
In 2025, AI tools are changing everything, including how we write code.
Yes, it can generate code, create features, or even scaffold entire apps for you, but that doesn't mean it is replacing real developers.
A significant part of software development involves understanding real-world problems, analyzing complex systems, and ensuring the codebase remains maintainable, scalable, and secure over time.
This takes human discretion. You can't just write a prompt and expect everything to be correct. It is important to actually understand the code and make corrections whenever necessary.
To put it simply, even if you are vibe coding, you need to be a good developer to become a good vibe coder.
What Is Full-Stack Web Development?
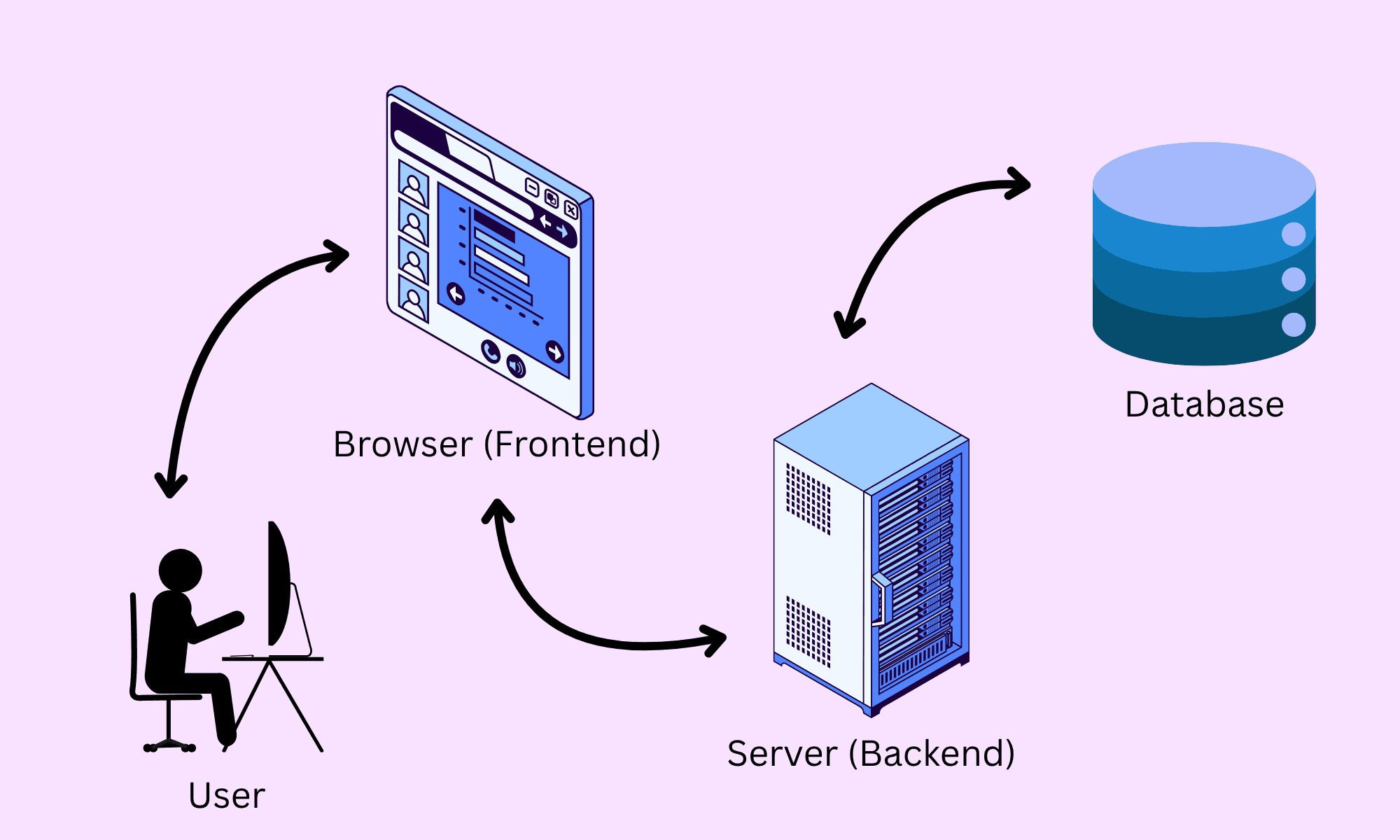
Full-stack web development means building both the frontend (client-side) and backend (server-side) of web applications, plus working with databases and APIs.
- Frontend: The part of the app users interact with directly. Built with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, often using frameworks like React.
- Backend: The server-side logic, APIs, and database interactions. Commonly built with backend languages such as Python, PHP, and of course, JavaScript, thanks to Node.js.
- Databases: Where your app stores and retrieves data. Some common choices include PostgreSQL, Supabase, Firebase, MongoDB, and so on.
What Skills Do You Need in 2025 to Become a Full-Stack Developer?
To become a full-stack developer in 2025, you should focus on these core skills:
Frontend
- HTML & CSS
- A CSS framework (TailwindCSS, BootstrapCSS)
- JavaScript
- React.js
Backend
- Node.js (JavaScript runtime)
- Express.js (Backend JavaScript framework)
- Database (Supabase, Firebase, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB)
- REST APIs (and optionally GraphQL)
Version Control
- Git (commits, branches, merging)
- GitHub (repositories, pull requests)
Deployment
- Vercel or Netlify (frontend hosting)
- Railway, Supabase, or Render (backend hosting)
Optional
- Authentication (Auth.js, Supabase Auth, Firebase Auth)
- API integration (fetch, axios)
- CI/CD basics (GitHub Actions, Vercel/Netlify pipelines)
Recommended Learning Path (Step-by-Step)
As a beginner, you are probably quite overwhelmed with so many different technologies.
But don't worry, here is a practical, project-based roadmap to becoming a full-stack developer in 2025.
We'll start with the most basic topics, building on each concept step by step, while you create real projects along the way.
1. Start with the Basics
Timeline: 1-2 weeks
- Learn HTML: structure, tags, forms, accessibility, etc.
- Learn CSS: selectors, box model, Flexbox, Grid, media queries, etc.
- Learn JavaScript fundamentals: variables, functions, loops, arrays, objects, DOM manipulation.
Projects:
- Create a calculator.
- Recreate the YouTube interface, or any other website you like.
- Build a personal landing page (about you, links, contact form).
2. Learn Git and GitHub
Timeline: 2-3 days
- Understand version control basics: what is Git, why use it.
- Learn common commands:
git init,add,commit,push,pull,clone. - Create a GitHub account and push your projects.
Projects:
- Create a new repo for each project.
- Practice making commits and pushing changes.
3. Build Interactive Frontends
Timeline: 2-3 weeks
- Dive into modern JavaScript: arrow functions, destructuring, modules, promises, asynchronous programming.
- Learn React.js: components, props, state, hooks (
useState,useEffect), React Router. - Understand component-based architecture.
Projects:
- Create an image slider with JavaScript.
- Create a drawing broad with JavaScript.
- Build a todo app with React (add, complete, delete tasks).
- Create a blog with React (list posts, view details).
4. Add Backend Knowledge
Timeline: 2-3 weeks
- Learn Node.js basics: modules,
npm, running a development server. - Use Express.js to build REST APIs (routes, middleware, controllers).
- Connect your backend to a database (PostgreSQL, Supabase or Firebase).
- Understand CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete).
Projects:
- Build a REST API system for a blog app.
- Create a React frontend and connect to your backend API.
5. Full-Stack Projects
Timeline: 2-4 weeks
- Combine your frontend and backend into a single app.
- Implement authentication (login/signup) using Auth.js or Supabase Auth.
- Add features like displaying user-specific data, file uploads, or notifications.
Projects:
- Build a full-stack CRUD app (task manager, CMS with auth).
- Build a small SaaS (habit tracker, expense tracker).
6. Learn Deployment & Hosting
Timeline: 1 week
- Deploy your frontend to Vercel or Netlify (connect your GitHub repo for auto-deploys).
- Deploy your backend to Railway, Supabase, or Render.
- Set up environment variables for API keys and secrets.
- Share your live project with others.
Common Mistakes Beginners Make
-
Jumping into frameworks too early: Don’t skip the basics of HTML, CSS, and vanilla JavaScript. Frameworks are easier to learn when you understand the fundamentals.
-
Not building projects: Theory is important, but real learning happens when you build and debug your own apps.
-
Not understanding the "why": Don’t just copy-paste code—ask yourself why each tool or library is used.
-
Skipping deployment: Deploying your projects teaches you about real-world issues and makes your work shareable.
Tools & Resources to Accelerate Your Learning
Code Editors
- VS Code – Most popular editor with great extensions.
- WebStorm – Powerful IDE for JavaScript and TypeScript.
- Sublime Text – Lightweight, fast, and customizable editor.
Free APIs
- Public APIs – Find APIs for practice projects.
- OpenWeatherMap – For weather dashboards.
- REST Countries – Country data for frontend projects.
- Unsplash API – Free images for your apps.
Browser DevTools
- Chrome DevTools, Firefox Developer Tools – Inspect, debug, and optimize your code.
- Lighthouse – Audit performance, accessibility, and SEO.
Online Coding Environments
- CodeSandbox, StackBlitz, Sandpack – Build and share projects instantly.
- Replit – Collaborative coding and hosting.
- GitHub Codespaces – Cloud development environments.
Design & UI Tools
- Figma – Collaborative interface design.
- Font Awesome – Free icons for web projects.
- Google Fonts – Free fonts for your sites.
Other Resources
- freeCodeCamp
- The Odin Project
- Supabase Docs
- Vercel Docs
- MDN Web Docs – Comprehensive documentation for various web technologies.
- Frontend Mentor – Real-world frontend challenges.
- Node.js Docs – Official Node.js documentation.
- React Docs – Official React documentation.
By following this roadmap, you’ll gain the skills to create modern web apps and stand out to employers or clients.
Remember, consistency beats speed, and every project you finish is a step closer to mastery.
Happy coding!