How to Customize Backgrounds Using CSS
Code Playground is only enabled on larger screen sizes.
You can customize the background of an element by setting background color, using images and gradients as the background, and more.
Color backgrounds
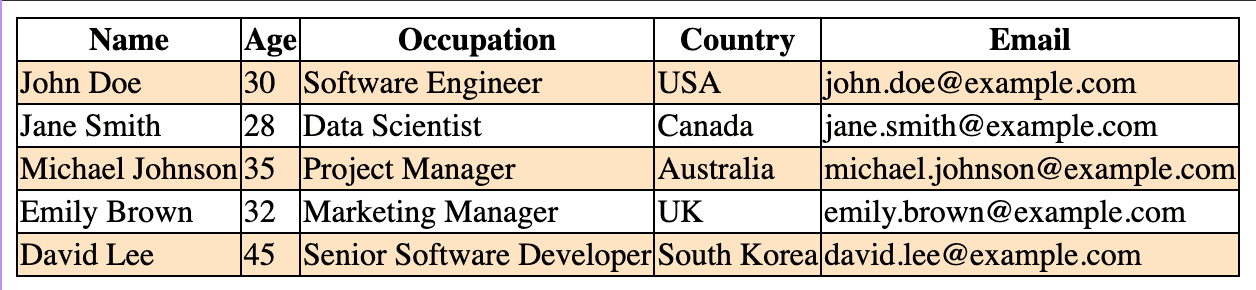
The background-color property adds a pure-color background. This is a commonly used method to draw users' attention to selected parts of the webpage.
For instance, you can highlight certain columns or rows in a table by specifying background colors.
<table>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Age</th>
<th class="highlight">Occupation</th>
<th>Country</th>
<th>Email</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>John Doe</td>
<td>30</td>
<td class="highlight">Software Engineer</td>
<td>USA</td>
<td>john.doe@example.com</td>
</tr>
. . .
</table>table {
border-collapse: collapse;
}
table,
th,
td {
border: 1px solid;
}
.highlight {
background-color: bisque;
}Zebra stripping
Another typical styling for tables is the zebra stripping.
Of course, you can micromanage individual rows in the table, but there is a better way by simply using the :nth-child pseudo-selector.
<table>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Age</th>
<th>Occupation</th>
<th>Country</th>
<th>Email</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>John Doe</td>
<td>30</td>
<td>Software Engineer</td>
<td>USA</td>
<td>john.doe@example.com</td>
</tr>
. . .
</table>table {
border-collapse: collapse;
}
table,
th,
td {
border: 1px solid;
}
tr:nth-child(even) {
background-color: bisque;
}By passing the parameter even, the styling will be applied to all even number rows of the table.
Colored backgrounds are also frequently combined with the :hover pseudo-selector to add more interactivity to the webpage.
For instance, in the following example, when the cursor is hovered over the table, the corresponding row will be highlighted.
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
}
table,
th,
td {
border: 1px solid;
}
tr:nth-child(even) {
background-color: bisque;
}
tr:hover {
background-color: orange;
}Image backgrounds
Besides pure-color backgrounds, it is also possible to create image-based backgrounds using the background-image property.
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit...</p>p {
background-image: url(https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1707843745563-d46b8ffb82fe?crop=entropy&cs=srgb&fm=jpg&ixid=M3wzMjM4NDZ8MHwxfHJhbmRvbXx8fHx8fHx8fDE3MDgwNzg4MjZ8&ixlib=rb-4.0.3&q=85);
}url() is a CSS function used to load external resources. It works similarly to the src attribute.
You can either load local image files like this:
url(/images/image.png)Or load remote files by specifying the full domain:
url(https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1707843745563-d46b8ffb82fe?crop=entropy&cs=srgb&fm=jpg&ixid=M3wzMjM4NDZ8MHwxfHJhbmRvbXx8fHx8fHx8fDE3MDgwNzg4MjZ8&ixlib=rb-4.0.3&q=85)Image size
Try the above demo in the playground, and you will see that the image is too big for the <p> element.
In this case, you can customize the size of the image using background-size.
p {
/* . . . */
background-image: url(. . .);
background-size: 100px;
/* background-size: <width>; */
/* background-size: <width> <height>; */
}If you don't know the size of the <div> element and want the browser to choose a size for you. You can use the keywords cover or contain.
p {
/* . . . */
background-image: url(. . .);
background-size: cover;
/* background-size: contain; */
}cover will make the image just large enough to cover the entire space of <div>, and contain will make the image just large enough to fit inside <div>.
Image repeat
By default, the image will be repeated both horizontally and vertically, if a single images is not enough to fill the entire <p> element's background.
You can turn off this behavior by setting background-repeat to no-repeat.
p {
/* . . . */
background-image: url(. . .);
background-size: contain;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}Or, in some cases, you might need to enable only horizontal or vertical repeat:
p {
/* . . . */
background-image: url(. . .);
background-size: contain;
background-repeat: repeat-x;
/* background-repeat: repeat-y; */
}Image position
Lastly, notice that the repeated background image always starts from the top left corner.
You can again customize this behavior by setting the background-position property, which takes two values, one horizontal position and one vertical position.
div {
/* . . . */
background-image: url(. . .);
background-size: 100px;
background-repeat: repeat;
background-position: bottom right;
}Gradient backgrounds
Gradients can also be used as the background.
In CSS, gradients are images generated with the functions linear-gradient(), radial-gradient(), or conic-gradient(). And because they are images, you must use the background-image property in this case.
<p class="linear-gradient">
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit...
</p>
<p class="radial-gradient">
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit...
</p>
<p class="conic-gradient">
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit...
</p>.linear-gradient {
background-image: linear-gradient(to right, #10b981, #06b6d4);
}
.radial-gradient {
background-image: radial-gradient(#10b981, #06b6d4);
}
.conic-gradient {
background-image: conic-gradient(#10b981, #06b6d4);
}The linear-gradient() function is the most commonly used option. It takes three parameters: the direction, the starting color, and the finishing color.
The direction can be either a numeric value in degrees (30deg, 60deg) or keywords such as to top, to bottom, and to left.
For the other two gradient functions, we will talk about them in detail later in the gradient lesson.
Background attachment
The last topic we must discuss regarding background is the background-attachment. It defines whether or not the background moves as the content scrolls.
The background-attachment property accepts two values, scroll or fixed.
- When set to
scroll, the background image will scroll with the content. - When set to
fixed, the background image will not move when the content scrolls.
<div class="fixed">
<!-- Make sure the paragraphs are long enough -->
<p>. . .</p>
<p>. . .</p>
<p>. . .</p>
</div>
<div class="scroll">
<!-- Make sure the paragraphs are long enough -->
<p>. . .</p>
<p>. . .</p>
<p>. . .</p>
</div>.fixed {
background-image: url(https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1706582748265-de941eeacfe6?crop=entropy&cs=srgb&fm=jpg&ixid=M3wzMjM4NDZ8MHwxfHJhbmRvbXx8fHx8fHx8fDE3MDgxNDc2MTV8&ixlib=rb-4.0.3&q=85);
background-size: contain;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-attachment: fixed;
}
.scroll {
background-image: url(https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1706582748265-de941eeacfe6?crop=entropy&cs=srgb&fm=jpg&ixid=M3wzMjM4NDZ8MHwxfHJhbmRvbXx8fHx8fHx8fDE3MDgxNDc2MTV8&ixlib=rb-4.0.3&q=85);
background-size: contain;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-attachment: scroll;
}The background shorthand
Lastly, background is a shorthand property for all background properties discussed above.
background: red;
background: url("/image.png") repeat-y;<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="/styles.css"> </head> <body> <table> <tr> <th>Name</th> <th>Age</th> <th class="highlight">Occupation</th> <th>Country</th> <th>Email</th> </tr> <tr> <td>John Doe</td> <td>30</td> <td class="highlight">Software Engineer</td> <td>USA</td> <td>john.doe@example.com</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Jane Smith</td> <td>28</td> <td class="highlight">Data Scientist</td> <td>Canada</td> <td>jane.smith@example.com</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Michael Johnson</td> <td>35</td> <td class="highlight">Project Manager</td> <td>Australia</td> <td>michael.johnson@example.com</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Emily Brown</td> <td>32</td> <td class="highlight">Marketing Manager</td> <td>UK</td> <td>emily.brown@example.com</td> </tr> <tr> <td>David Lee</td> <td>45</td> <td class="highlight">Senior Software Developer</td> <td>South Korea</td> <td>david.lee@example.com</td> </tr> </table> </body> </html>